Vietnam is now a popular investment destination for many foreigners. When a foreigner begins to live in Vietnam, he/she must pay the tax correctly in Vietnam according to the Vietnamese personal income tax system (progressive taxation system).
Points to keep in mind about personal income tax (PIT) for foreigners in Vietnam
Regarding Vietnam's personal income tax, the point to keep in mind is whether you are a tax resident or a non-resident.
As a matter of course, tax residents will have to pay taxes according to the Vietnamese tax system. The point to note isEven for non-residents, for income received as a result of working in Vietnam,
There is an obligation to pay tax according to a certain tax rate (depending on the amount of income and tax year). It is also necessary to keep in mind that if you pay taxes in Vietnam as a consideration for temporary work in Vietnam, foreign tax credits can be applied in your home country.
Vietnam personal income tax (PIT) filing
Income tax (PIT) range
The personal income tax (PIT) tax rate will progressively increase from 5% to 35% depending on your income. The tax applies to all forms of income, including dividends (excluding government bonds), interest (excluding bank deposits and life insurance), prizes, prizes and land transfers. If you are considered to be resident in Vietnam, you must declare and pay tax not only within Vietnam but also outside Vietnam.
Whether income tax is reported (judgment of residence)
If you become a tax resident in Vietnam, it is important to determine if you are a tax resident, as there is an obligation to declare the tax. One of the important things to consider when you are determined to be a tax resident is the length of your stay in Vietnam.
You are considered a resident if you stay in Vietnam for more than 183 days. When the number of days is less than 183 days, various points are considered and judged, such as being treated as residence (presence or absence of fixed residence, employment etc.). For more information on resident determination, we recommend consulting with a Vietnamese accountant or Vietnamese lawyer.
Tax rate of personal income tax in Vietnam
The personal income tax (PIT) rates for Vietnam are as follows:
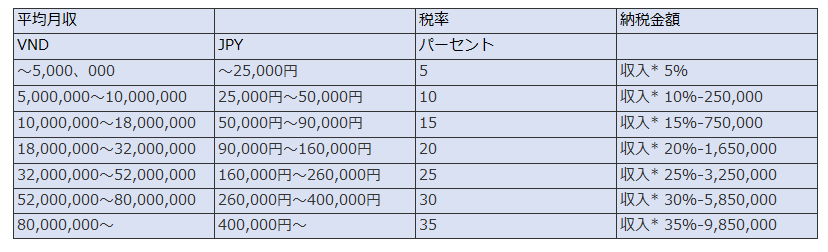
Vietnam income tax rate
- VND 0-60,000,000: 5%
- VND 60,000,001 – 120,000,000: 10%
- VND 120,000,001 – 216,000,000: 15%
- VND 216,000,001 – 384,000,000: 20%
- VND 384,000,001 – 624,000,000: 25%
- VND 624,000,001 – 960,000,000: 30%
- Over 960,000,001 Dong: 35%
* Specific deductions are available for children under the age of 18, unemployed spouses, older parents, charitable donations, etc.
*For non-residents, 20% is levied on income from Vietnam.
* If you have a corporation, there is a separate corporation income tax in addition to the individual income tax, and it is subject to 20-50% taxation.
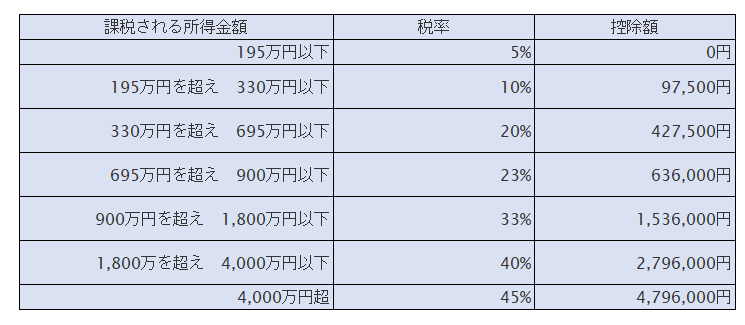
Income tax rate in Japan
Vietnam's income tax is high
Vietnam's income tax is much higher than Japan's tax rate.
From the table above, if the monthly salary is 400,000 yen or more (5.2 million yen for 13 months annual income), the tax rate of 35% will be applied in Vietnam. On the other hand, in Japan, the tax burden is only 20%. The difference is 15%, which is 780,000 yen, which is 15% of 5.2 million yen. This is a calculation that completely omits basic deductions, etc., but I can not say unequivocally, but it will be a difference of 300,000 to 400,000 yen.
Vietnam personal income tax (PIT) deduction

Vietnam personal income tax (PIT) basic deduction
Basic deduction: VND 9 million/month
*All tax residents are automatically eligible for this benefit.
Deduction for dependents: 3.6 million dong/month for each dependent
*Taxpayers are required to receive the tax exemption for dependents.You must register a qualified dependent and provide supporting documentation to the tax authorities..
Other deductions for personal income tax (PIT) in Vietnam
Other deductibles include:
- Contribution to social insurance, health insurance and unemployment insurance
- Contribution to pension system
- Contribution of compulsory social insurance system overseas
- Donation to charity
Exemption from personal income tax (PIT) in Vietnam
In addition to executive and employment income, income subject to Vietnam's personal income tax is also subject to compensation handed in cash and benefits in kind. However, the following are not taxable:
What is not included in taxable items
- Travel expenses
- Phone charges/stationery costs
- Office clothes
- Travel expenses and temporary allowance between Vietnam and overseas
- Round trip transportation to work
- Airfare for employees working in shifts in many industries (eg oil, mining)
- Cash received at weddings and funerals (with a limit)
Summary of personal income tax (PIT) of foreigners in Vietnam
The rate of personal income tax in Vietnam is very high. According to one theory, most of Vietnam's income tax income comes from foreigners and expatriates living in Vietnam. Perhaps because of this, taxation on foreigners in Vietnam is being tightened year by year.
If you are unfamiliar with Vietnam's tax filings, you may be subject to unexpected additional taxes and penalties. Therefore, we recommend that you consult a specialist who is familiar with Vietnamese law and tax affairs.
You can calculate your salary (take-home) from the following personal income tax and social insurance premium calculation app.

Residential land and building trader. After working at the largest Japanese accounting office in Hong Kong, he was founded independently in Vietnam.
In Ho Chi Minh City, together with fellow Vietnamese accountants, we provide real estate, accounting, taxation, auditing, and one-stop services to foreign-affiliated companies including Japanese companies.